



| SIZE (MM) | NORMAL WEIGHT (KG/ METRE) | TOLERANCE (KG/METRE) | BUNDLE WEIGHT (KG) | NUMBER OF PIECES (NO.) | BHARATHI TOLERANCE (KG/METRE) | BHARATHI BUNDLE WEIGHT (KG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.222 | 0.204-0.238 | 49.440-57.120 | 20 | 0.226 - 0.232 | 55.5 - 57.0 |
| 8 | 0.395 | 0.367-0.423 | 44.040-50.760 | 10 | 0.370 - 0.377 | 45.5 - 47.0 |
| 10 | 0.617 | 0.574-0.660 | 48.220-55.440 | 7 | 0.575 - 0.595 | 50.0 - 51.5 |
| 12 | 0.888 | 0.844-0.932 | 50.580-55.920 | 5 | 0.865 - 0.885 | 52.5 - 54.0 |
| 16 | 1.578 | 1.500-1.656 | 53.965-59.650 | 3 | 1.500 - 1.530 | 55.5 - 57.5 |
| 20 | 2.470 | 2.400-2.540 | 57.435-60.960 | 2 | 2.410 - 2.460 | 58.5 - 60.5 |
| 25 | 3.854 | 3.740-3.969 | 44.860-47.630 | 1 | 3.750 - 3.900 | 45.5 - 47.5 |
| 32 | 6.310 | 6.120-6.499 | 73.450-77.980 | 1 | 6.200 - 6.350 | 75.5 - 77.5 |
Bharathi TMT bars display improved mechanical properties like high yield strength, ductility, toughness, etc
| MECHANICAL PROPERTIES | UNIT | IS:1786 FE550 (BIS) ) | BHARATHI TMT FE550 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | N/mm2 (Min) | 550 | 570 |
| Tensile Strength | N/mm2 (Min) | 600 | 660 |
| UTS / YS Ratio | (Min) | 1.06 | 1.14 |
| Elongation | % (Min) | 14.5 | 17.5 |
| Total Elongation | % (Min) | 5 | 5 |
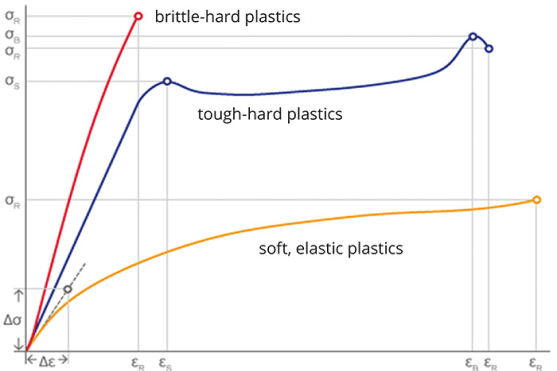
Comparison by soft / hard

Bharathi TMT maintains the requisite levels of carbon as specified by BIS standards. Impurities such as sulphur and phosphorous that reduce the durability of steel are also maintained at recommended BIS levels.
| ELEMENTS | IS:1786 FE550 (BIS) | BHARATHI TMT FE550 |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 0.25 (Max) | 0.20- 0.24 (Max) |
| Phosphorous | 0.045 (Max) | 0.04 (Max) |
| Sulphur | 0.045 (Max) | 0.035 (Max) |
| Manganese | NA | 0.65 (Min) |
| CE | 0.5 (Max) | 0.42 (Max) |
Carbon is essential for the formation of cementite, pearlite, spheroidite, bainite and iron-carbon martensite, with martensite being the hardest of the microstructures. Carbon is also responsible for increase in tensile strength and hardness